# API Authentication
# Endpoint Management
# Create Endpoint
If you need to enable API authentication, select OpenAPI for partners when creating an endpoint.
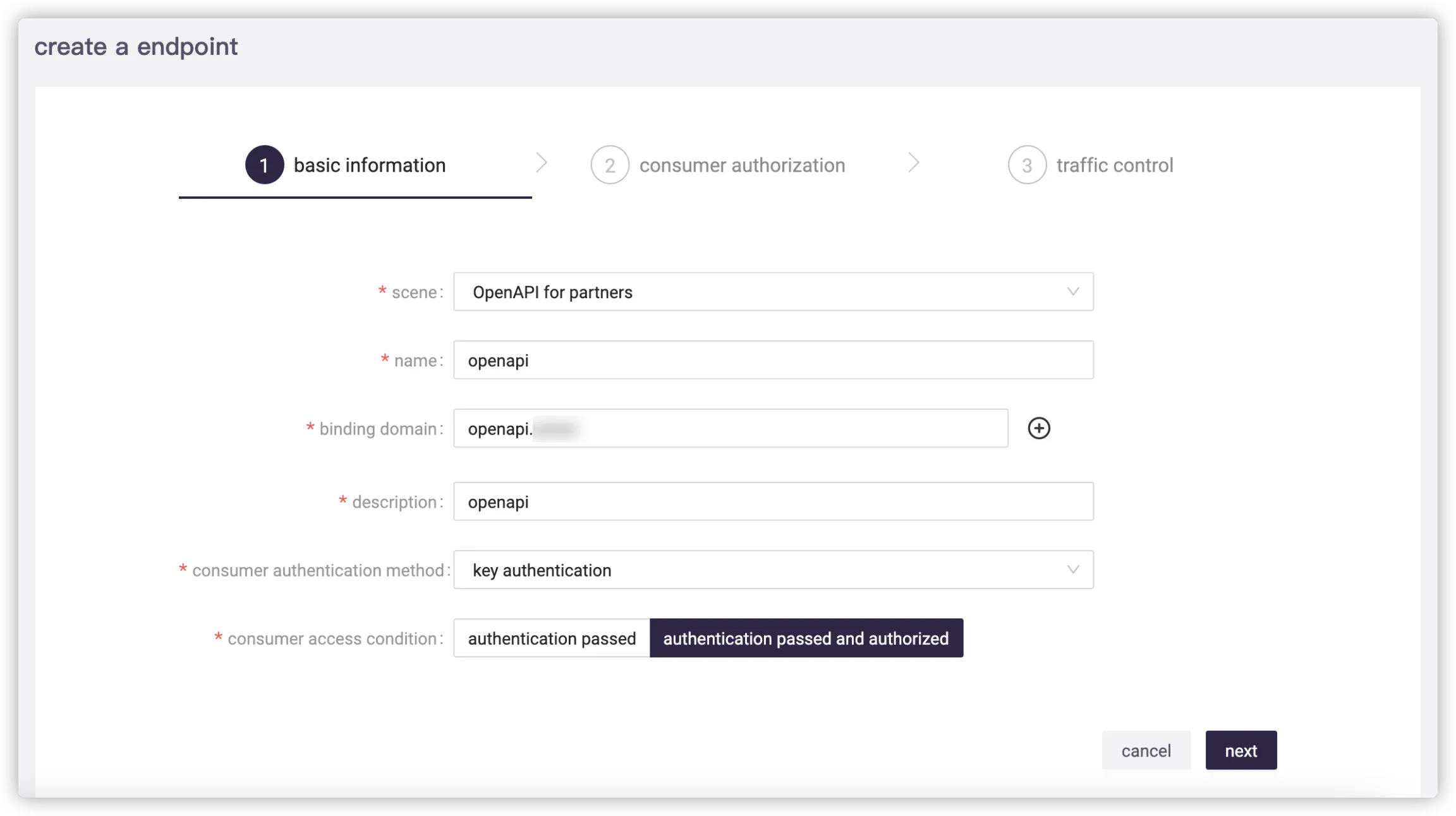
Consumer Authentication Method
- Key authentication: Identify consumers through the
appKeyfield in the request parameters or theX-App-Keyin the request header. - HMAC authentication: Use HMAC to encrypt the request line, request header, and request body with high security, and it is designed according to the draft of HTTP signature algorithm standard with versatility. For details, see HMAC Signature Authentication.
- Parameter signature authentication: Identify consumers through the
appKeyfield in the request parameters, and verify through thesignfield of signature. For details, see Parameter Signature Authentication. - OAuth2 authentication: Identify consumers through a dynamic token based on the OAuth2 client credentials mode, with a library similar to
Spring Cloud Security.
Consumer Access Condition
- Authentication passed: Only needs the correct certificate to pass identification for access.
- Authentication passed and authorized: Needs additional authorization for the consumer to access.
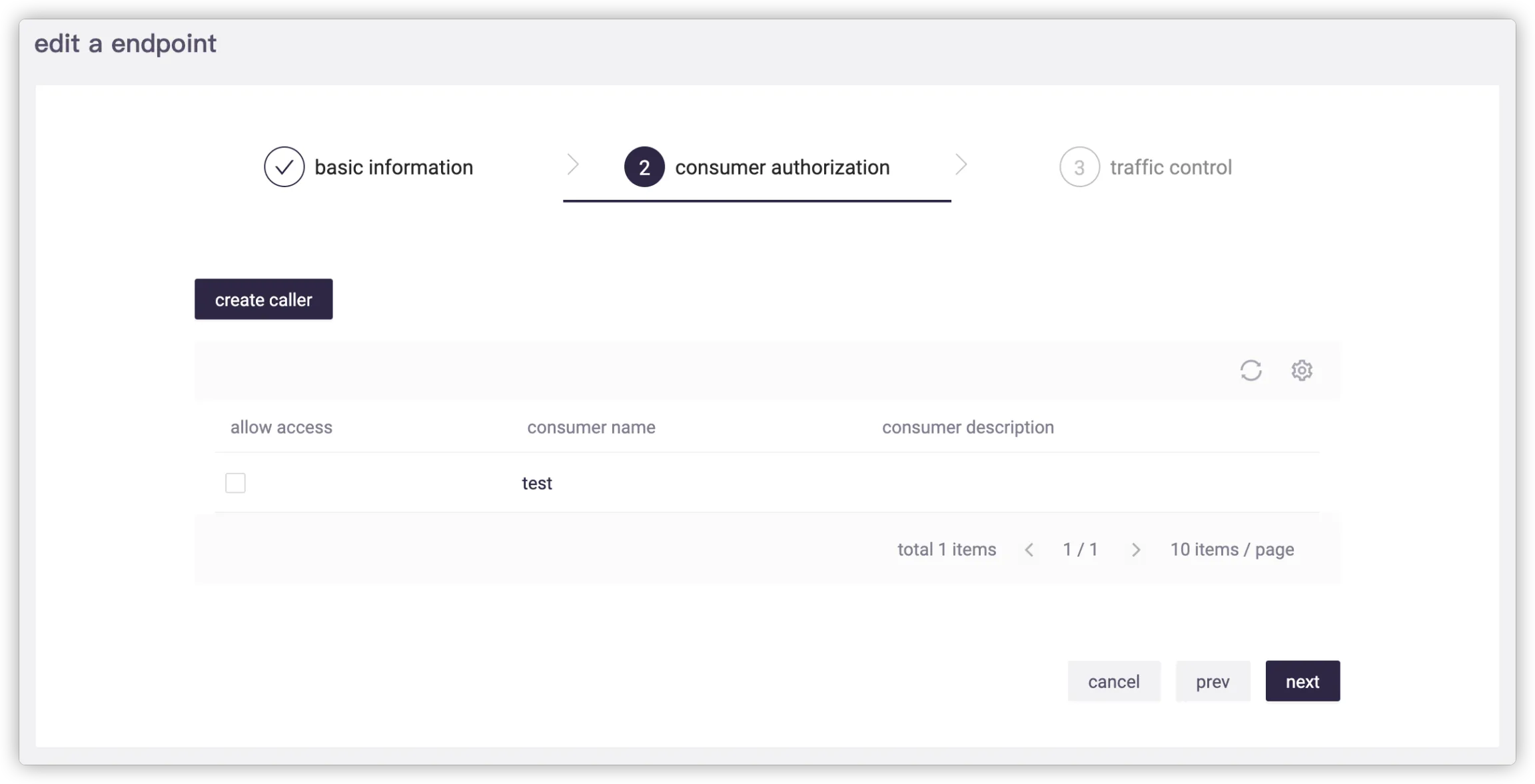
# Consumer Authorization
If select Authentication passed and authorized for consumer access condition, the consumer authorization is required.
You can complete consumer authorization when creating the endpoint, or finish it by endpoint editing later.
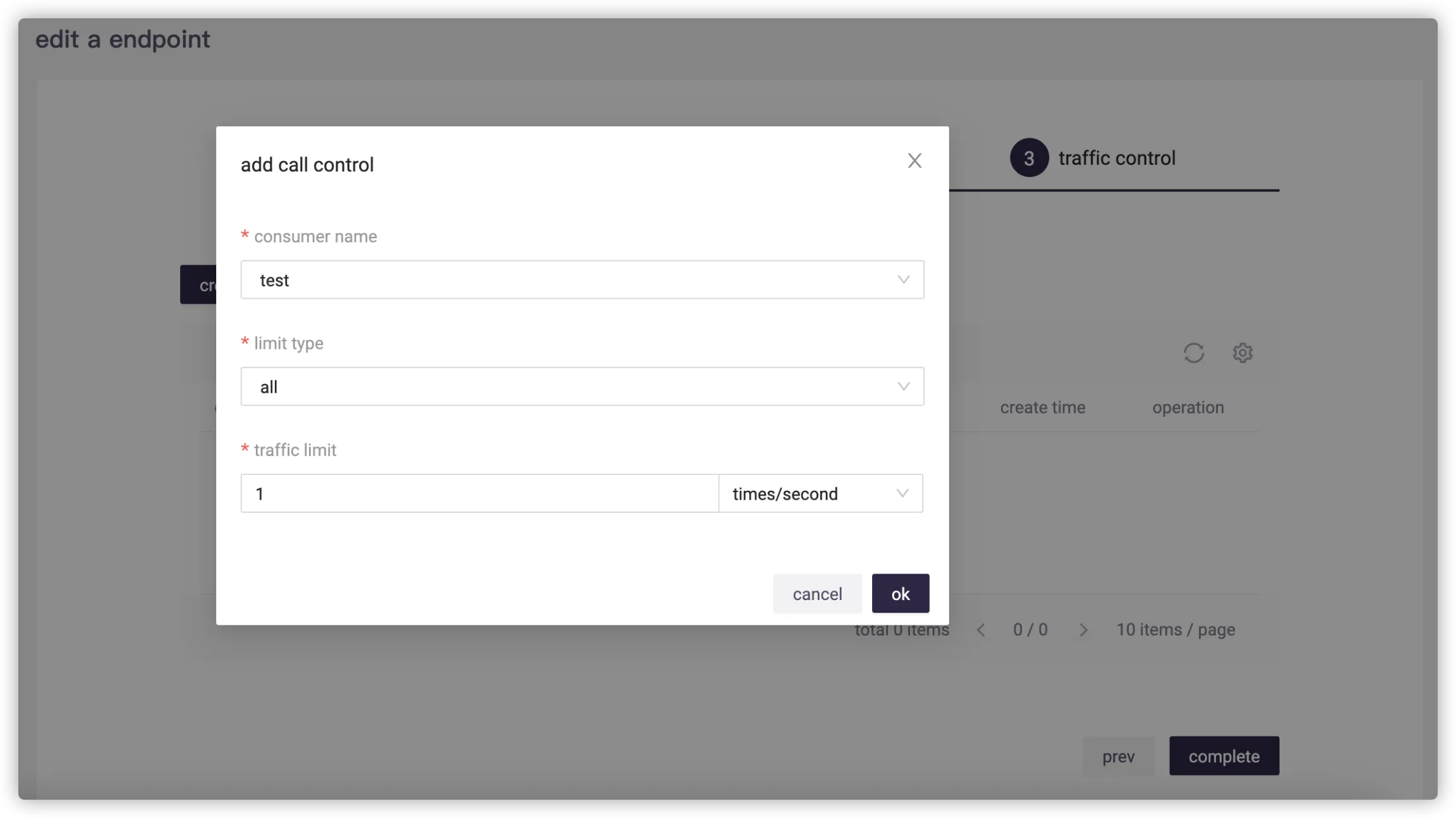
# Traffic Control
You can complete traffic control when creating the endpoint, or finish it by endpoint editing later.
# Consumer Certificate Management
Select a consumer and click Certificate.
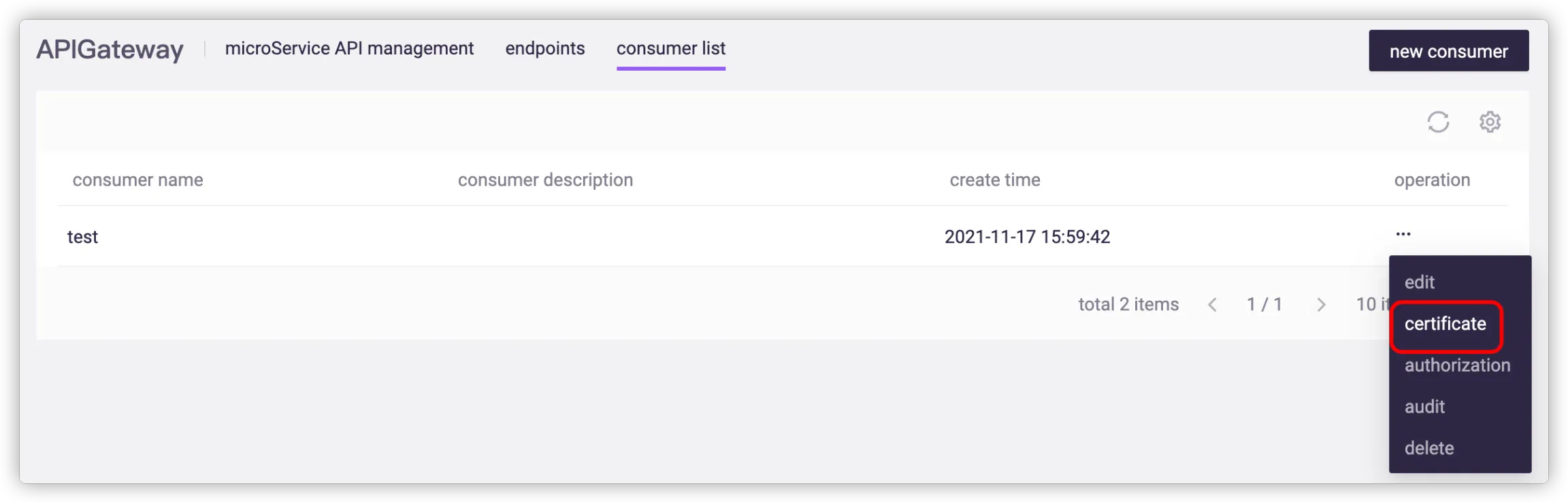
The consumer will select the correct certificate according to the authentication method of the endpoint.

# Signature Authentication Algorithm
Among the authentication methods provided by the platform, both HMAC signature authentication and parameter signature authentication can identify the consumer and check the signature of the request parameters and body to further ensure that the request has not been tampered with or forged.
# HMAC Signature Authentication (Recommended)
The algorithm is mainly based on the HTTP Signature Draft (opens new window) and uses Kong's native HMAC-Auth plugin (opens new window).
# Authorization Request Header
An example of a standard authorization request header is as follows:
Authorization: hmac appkey="wsK8t77fvAAs3i7878NSkC0j95ib3oVu", algorithm="hmac-sha256", headers="date request-line", signature="gaweQbATuaGmLrUr3HE0DzU1keWGCt3H96M28sSHTG8="
HMAC
Indicates the use of HMAC signature, which is a static field that is consistent across all requests and does not need to be changed.
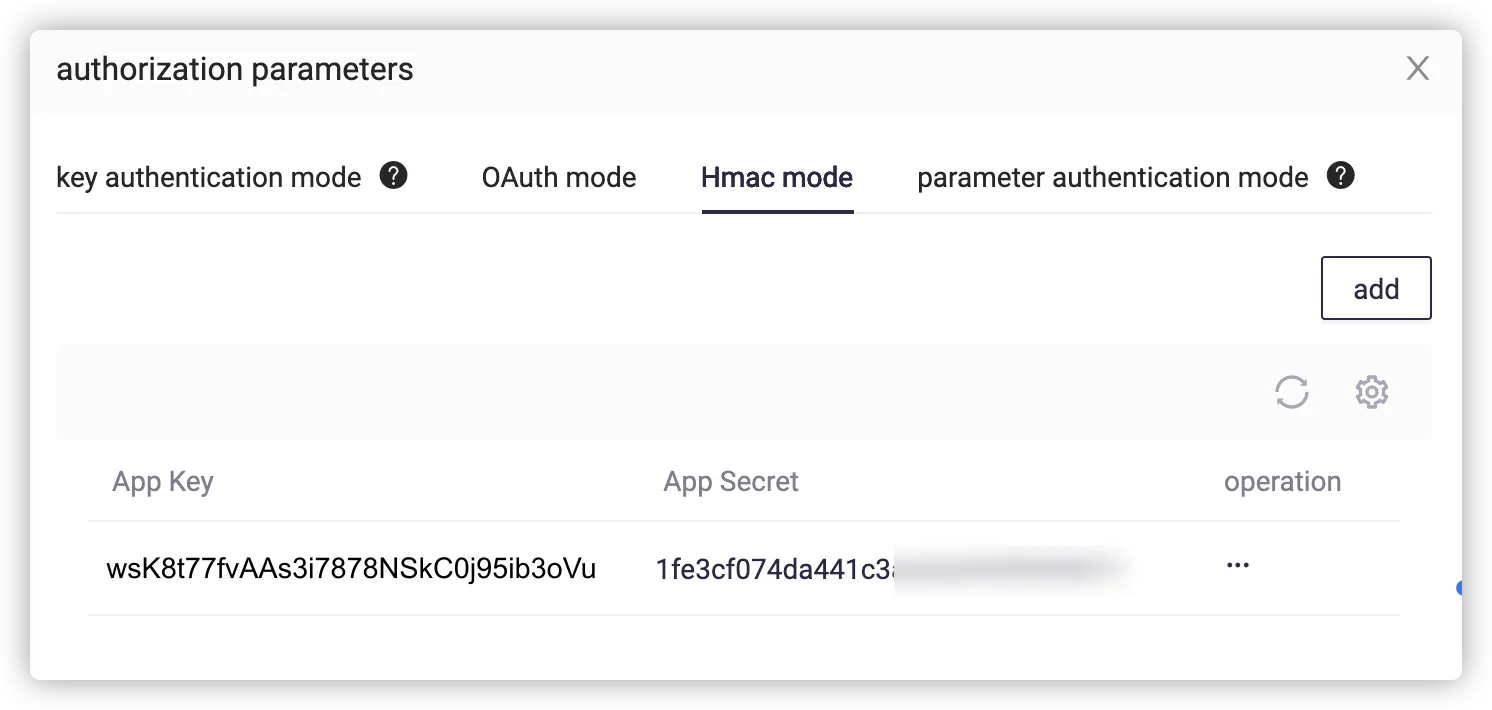
appkey="wsK8t77fvAAs3i7878NSkC0j95ib3oVu"
That is, the App Key field in the certificate (shown below) needs to be separated from HMAC by ASCII spaces
.
algorithm="hmac-sha256"
Indicates the signature algorithm used, which does not need to be changed and should be separated from the appkey by ASCII characters
,and ASCII spaces.headers="date request-line"
The request headers involved in the signature are all lowercase and ordered, indicating the order of field splicing during the signature process (for details, see Signature Algorithm), and need to be separated from the algorithm by ASCII characters
,and ASCII spaces.Tips
The field
request-lineis relatively special, indicating the request line, such asGET /api?name=bob HTTP/1.1, which is not a header although it is written in headers.signature="gaweQbATuaGmLrUr3HE0DzU1keWGCt3H96M28sSHTG8="
The signature value generated based on the signature algorithm must be separated from headers by ASCII characters
,and ASCII spaces.
# Signature Algorithm
- Request body not exist
Required request header
- Date
- Authorization
Date request header
The date request header needs to follow the RFC1123 HTTP specification, such as
Thu, 10 Dec 2020 08:47:43 GMT.Generated by Unix command:
env LANG=eng TZ=GMT date '+%a, %d %b %Y %T %Z'
Tips
If the absolute difference between the date request header time and the server time is greater than 5 minutes, it will be considered as a replay request and will be rejected.
Authorization request header
For the request header structure, see Authorization Request Header. The following will introduce how to generate a signature.
For example, for the following request:
curl -i -X GET http://localhost/requests?name=bob \ -H 'Host: hmac.com' \ -H 'Date: Thu, 22 Jun 2017 21:12:36 GMT' \ -H 'Authorization: hmac appkey="wsK8t77fvAAs3i7878NSkC0j95ib3oVu", algorithm="hmac-sha256", headers="date host request-line", signature="FiPTWoayUGvlaAk6HbnxEzlXo0JO2HhiDGEwsR4yKPo="'The authorization header specifies the request headers for signing,
date,host,and the special request linerequest-line, and splices the strings to obtain the string to be signed:date: Thu, 22 Jun 2017 21:12:36 GMT host: hmac.com GET /requests?name=bob HTTP/1.1The rules for signing the string as follows:
signed_string=HMAC-SHA256(<signing_string>, "secret") signature=base64(<signed_string>)If the App Secret is
qdWre3pJxitNm9NOBRH3EpWeVYepnt3f, the get the signature value asFiPTWoayUGvlaAk6HbnxEzlXo0JO2HhiDGEwsR4yKPo=.Use Unix commands to generate the signature:
echo -ne "date: Thu, 22 Jun 2017 21:12:36 GMT\nhost: hmac.com\nGET /requests?name=bob HTTP/1.1" | \ openssl dgst -sha256 -hmac "qdWre3pJxitNm9NOBRH3EpWeVYepnt3f" -binary | base64
- Request body exists
Required request header
- Date
- Digest
- Authorization
Date request header
The date request header needs to follow the RFC1123 HTTP specification, such as
Thu, 10 Dec 2020 08:47:43 GMT.Digest request header
Use SHA-256 to sign the request body. For example, if the body is
{"name": "bob"}, then the corresponding digest request header isDigest: SHA-256=lWuihDRnfX2CUVffGA74EjBnzVgnfHPywPXkYaKDC1I=, where thevalueof the digest request header needs to start withSHA-256=.Generated by Unix command:
echo -n '{"name": "bob"}' | openssl dgst -sha256 -binary | base64Request limit: The request body size should not exceed 10 m.
Authorization request header
The headers must include the digest. An example is as follows:
curl -i -X POST http://localhost/requests \ -H 'Host: hmac.com' \ -H 'Date: Thu, 22 Jun 2017 21:12:36 GMT' \ -H 'Digest: SHA-256=956ba28434677d7d825157df180ef8123067cd58277c73f2c0f5e461a2830b52' \ -H 'Authorization: hmac appkey="wsK8t77fvAAs3i7878NSkC0j95ib3oVu", algorithm="hmac-sha256", headers="date request-line digest", signature="CZSUv+kxWHN/vPEbwARg4r+NN3Vnb9+Aaq5XOQiENJA="' -d '{"name": "bob"}'The authorization header specifies the request headers for signing,
date,host, the special request linerequest-line,and the signature valuedigestof the request body, and splices the strings to obtain the string to be signed:date: Thu, 22 Jun 2017 21:12:36 GMT GET /requests?name=bob HTTP/1.1 digest: SHA-256=lWuihDRnfX2CUVffGA74EjBnzVgnfHPywPXkYaKDC1I=For the method to generate the signature, see Request body not exist.
# Code Example 1: Implementation of HMAC Authentication for Post Request Client with Body in Java Language
Tips
This example contains only the code to generate the necessary request parameters, not the code to initiate the HTTP request.
import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Base64;
import org.apache.commons.codec.digest.HmacAlgorithms;
import org.apache.commons.codec.digest.HmacUtils;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZoneOffset;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.Locale;
public class HmacTest {
private static final String APP_KEY = "088ed68d41504123b76d0812f328b560";
private static final String APP_SECRET = "01c28076047a46a9a3d46d9082f2a716";
private static final String URI = "/requests?name=bob";
public static void main(String[] args) {
String requestBody = "{\"name\": \"bob\"}";
// generate date
// Note: When the date is earlier than 10, the string formatted with RFC_1123_DATE_TIME will be considered an error due to the omission of the zero on the tens digit.
DateTimeFormatter timeFormatter = DateTimeFormatter
.ofPattern("EEE, dd MMM yyyy HH:mm:ss z", Locale.ENGLISH)
.withZone(ZoneId.of("GMT"));
String date = timeFormatter.format(ZonedDateTime.now(ZoneOffset.UTC));
// generate digest
MessageDigest messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-256");
messageDigest.update(requestBody.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8));
String digest = "SHA-256=" + Base64.encodeBase64String(messageDigest.digest());
// generate signature
String signStrFormat = "date: %s\n%s %s HTTP/1.1\ndigest: %s";
String signStr = String.format(signStrFormat, date, "POST", URI, digest);
String signature = Base64.encodeBase64String(new HmacUtils(HmacAlgorithms.HMAC_SHA_256, APP_SECRET).hmac(signStr));
// generate Authorization
String authorizationFormat = "hmac appkey=\"%s\", algorithm=\"hmac-sha256\", headers=\"date request-line digest\", signature=\"%s\"";
String authorization = String.format(authorizationFormat, APP_KEY, signature);
System.out.println("signStr: \n" + signStr);
System.out.println("Date: " + date);
System.out.println("Digest: " + digest);
System.out.println("Authorization: " + authorization);
// When initiating an HTTP request, set the date, digest, and authorization printed above to the request header
}
}
# Code Example 2: Implementation of HMAC Authentication for Post Request Client with Body in Go Language
Tips
This example contains the complete code to generate the necessary parameters and initiate the HTTP request.
package main
import (
"bytes"
"crypto/hmac"
"crypto/sha256"
"encoding/base64"
"fmt"
"io/ioutil"
"log"
"net/http"
"time"
)
func main() {
const (
body = `{"name": "bob"}`
appKey = "088ed68d41504123b76d0812f328b560"
appSec = "01c28076047a46a9a3d46d9082f2a716"
host = "https://go-http-demo-auth.daily.terminus.io"
uri = "/requests?name=bob"
)
request, err := http.NewRequest(http.MethodPost, host+uri, bytes.NewBufferString(body))
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to NewRequest: %v", err)
}
if err = hmacRequest(request, appKey, appSec); err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to hmacRequest: %v", err)
}
response, err := http.DefaultClient.Do(request)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to Do: %v", err)
}
data, err := ioutil.ReadAll(response.Body)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to ReadAll: %v", err)
}
fmt.Printf("response body: %s", string(data))
}
// Digest implements the digest algorithm for body
// Note: When calculating the signature, encode from binary to string with Base64 method
func digest(data []byte) (string, error) {
h := sha256.New()
if _, err := h.Write(data); err != nil {
return "", err
}
return "SHA-256=" + base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(h.Sum(nil)), nil
}
// Date gets the log needed for signature calculating, note that location is Europe/London time, with time format of RFC1123
func date() (string, error) {
location, err := time.LoadLocation("Europe/London")
if err != nil {
return "", err
}
return time.Now().In(location).Format(time.RFC1123), nil
}
// Signature is generated based on the given date, method, reqeustLine, digest and appSecret
func signature(date, method, requestLine, digest, appSecret string) (signString, sign string, err error) {
signString = fmt.Sprintf("date: %s\n%s %s HTTP/1.1\ndigest: %s", date, method, requestLine, digest)
h := hmac.New(sha256.New, []byte(appSecret))
if _, err := h.Write([]byte(signString)); err != nil {
return signString, "", err
}
sign = base64.StdEncoding.EncodeToString(h.Sum(nil))
return signString, sign, nil
}
// authorization constructs the value of the request header authorization
func authorization(appKey, sign string) string {
const authorizationPat = `Authorization: hmac appkey="%s", algorithm="hmac-sha256", headers="date request-line digest", signature="%s"`
return fmt.Sprintf(authorizationPat, appKey, sign)
}
// hmacRequest puts the calculated date, digest, signature, etc. into the headers of *http.Request
func hmacRequest(r *http.Request, appKey, appSecret string) error {
body, err := r.GetBody()
if err != nil {
return err
}
// read body
data, err := ioutil.ReadAll(body)
if err != nil {
return err
}
// make digest
digest, err := digest(data)
if err != nil {
return err
}
fmt.Printf("digest: %s\n", digest)
// make date
date, err := date()
if err != nil {
return err
}
fmt.Printf("date: %s\n", date)
// make signature
signString, sign, err := signature(date, r.Method, r.URL.RequestURI(), digest, appSecret)
if err != nil {
log.Fatalf("failed to sinature: %v", err)
}
fmt.Printf("signString: %s\n", signString)
fmt.Printf("sign: %s\n", sign)
// make auth
author := authorization(appKey, sign)
fmt.Printf("authorization: %s\n", author)
// set headers
r.Header.Set("date", date)
r.Header.Set("digest", digest)
r.Header.Set("Authorization", author)
return nil
}
# Parameter Signature Authentication
All parameters (including appKey, but not the signature parameter sign itself) are arranged in increasing order of characters, and then add appSecret to the end of the arranged parameter string, and sign the complete string with SHA512 to generate the signature parameter sign.
# Signature Based on URL Parameter
For example, the call parameters are:
/api?appKey=foobar&name=dadu&abc=123
The parameter names are sorted in ascending alphabetical order to get:
abc=123&appKey=foobar&name=dadu
Assuming that the App Secret in the calling certificate is my.secret and add it to the end of the parameter to get:
abc=123&appKey=foobar&name=dadumy.secret
Calculate the SHA512 of the string, and get the signature value:
f97efc239eef4eafe69bfe41438740199d939e2e123c4c5a6b5d0b5e58d295a2818d6444c5c7b9e5985e751ad93f9c854e1966e59a63a1eeceb31e46641e291a
The final request is:
/api?appKey=foobar&name=dadu&abc=123&sign=f97efc239eef4eafe69bfe41438740199d939e2e123c4c5a6b5d0b5e58d295a2818d6444c5c7b9e5985e751ad93f9c854e1966e59a63a1eeceb31e46641e291a
# Signature Based on Body
For requests with body such as post, the body will be signed. There are two situations:
Content-Type is
application/x-www-form-urlencodedIt is the same as the URL parameter signature, to put parameters into the body.
Request limit:
- The body size does not exceed 10 m.
- The number of parameters is not greater than 100.
Content-Type is
application/jsonFor example, the original request is:
POST --header 'Content-Type: application/json' -d ' {"userName":"abc","gender":"male"} 'Take the body as a parameter named Data and arrange them in ascending alphabetical order to get:
appKey=foobar&data={"userName":"abc","gender":"male"}Assuming that the App Secret in the calling certificate is
my.secretand add it to the end of the parameter to get:appKey=foobar&data={"userName":"abc","gender":"male"}my.secretCalculate the SHA512 of the string, and get the signature value:
ec23eeda5f88abe26311ed020439172eea409e3475875c87e9abfa8a6856138e767608e8497435f573ccb417a90448c78abdca4a0de12c4da4583aa3add7bf52The final request is:
POST --header 'Content-Type: application/json' -d ' { "data": "{\"userName\":\"abc\",\"gender\":\"male\"}", "appKey": "foobar", "sign": "ec23eeda5f88abe26311ed020439172eea409e3475875c87e9abfa8a6856138e767608e8497435f573ccb417a90448c78abdca4a0de12c4da4583aa3add7bf52" }'After the gateway receives the request, the real request sent to the back-end service is the same as the original request:
POST --header 'Content-Type: application/json' -d ' {"userName":"abc","gender":"male"} 'Request limit: The body size does not exceed 2 m.
# Signature with Timestamp (Optional)
Add a timestamp parameter named apiTimestamp and sign it together with other parameters in ascending order to generate sign.
Timestamp value
Unix timestamp standard: the number of seconds elapsed since January 1, 1970 (midnight UTC/GMT)
How to obtain by different languages:
Java System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000 JavaScript Math.round(new Date().getTime()/1000) Time verification
After adding the timestamp parameter
apiTimestamp, the gateway will determine whether the time is close to the server side, allowing a positive or negative error within 5 minutes, otherwise, the authentication will fail.Example
Take the URL parameter signature as an example:
/api?appKey=foobar&name=dadu&abc=123Add the parameter
apiTimestamp=1581565619, sort in ascending character order, and add App Secret (assumingmy.secret):abc=123&apiTimestamp=1581565619&appKey=foobar&name=dadumy.secretCalculate the SHA512 of the string, and get the signature value:
61cabbc719e5edff3021ab5047bd3c5981e6348066d0416254dd529241a7135d57498dac56d2400139bc1040c5759d1c0798f1673913c537d10769c149879eddThe final request is:
/api?appKey=foobar&name=dadu&abc=123&apiTimestamp=1581565619&sign=61cabbc719e5edff3021ab5047bd3c5981e6348066d0416254dd529241a7135d57498dac56d2400139bc1040c5759d1c0798f1673913c537d10769c149879eddCarry
apiTimestampin the JSON structure of the body. For example:POST --header 'Content-Type: application/json' -d ' { "data": "{\"userName\":\"abc\",\"gender\":\"male\"}", "appKey": "foobar", "apiTimestamp": 1581565619, "sign": "xxxx", }'
# Code Sample
Signature generation:
// SignAuthHelper.Java
import org.apache.commons.codec.binary.Hex;
import org.apache.commons.lang.StringUtils;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.security.NoSuchAlgorithmException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.security.MessageDigest;
import java.util.stream.Collectors;
/**
* SignAuthHelper.java (JAVA 8+)
*/
public class SignAuthHelper {
public static Map<String, String> sign(Map<String,String> args, String appSecret) {
args.put("appKey", args.get("appKey"));
List<String> keyList = args.entrySet().stream().map(Map.Entry::getKey).sorted().collect(Collectors.toList());
List<String> kvList = new ArrayList<>();
for (String key: keyList) {
kvList.add(key + "=" + args.get(key));
}
String argsStr = StringUtils.join(kvList, "&") + appSecret;
String sign = string2SHA512(argsStr);
args.put("sign", sign);
return args;
}
private static String string2SHA512(String str) {
MessageDigest messageDigest;
String encdeStr = "";
try {
messageDigest = MessageDigest.getInstance("SHA-512");
byte[] hash = messageDigest.digest(str.getBytes("UTF-8"));
encdeStr = Hex.encodeHexString(hash);
} catch (NoSuchAlgorithmException | UnsupportedEncodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return encdeStr;
}
}
Test procedure:
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import static org.junit.Assert.assertEquals;
/**
* Main.java (JAVA 8+)
*/
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Sign Request URL Parameter
// GET https://domain.com?param1=123¶m2=Abc&appKey=foobar&pampasCall=query.coupon
Map<String, String> params = new HashMap<>(2);
params.put("param1", "123");
params.put("param2", "Abc");
params.put("appKey", "foobar");
params.put("pampasCall", "query.coupon");
params = SignAuthHelper.sign(params, "my.secret");
String expect = "d6fee3145be668425f70878084f9d"
+ "39fce3f7c5fca283ffc4c5d5a5568077334e9a505"
+ "26e7e806758a66b7647ae9951f9324a0f921e28417e07d69beed79f7ef";
assertEquals(expect, params.get("sign"));
System.out.println("Verify Success");
// Sign Request Body
// POST --header 'Content-Type: application/json'
// --header 'Accept: application/json'
// -d '{"userName":"abc","gender":"male"}'
// 'https://domain.com'
params = new HashMap<>(4);
// request body use data as param name
params.put("data", "{\"userName\":\"abc\",\"gender\":\"male\"}");
params.put("appKey", "foobar");
expect = "ec23eeda5f88abe26311ed020439172eea409e34"
+ "75875c87e9abfa8a6856138e767608e8497435f573c"
+ "cb417a90448c78abdca4a0de12c4da4583aa3add7bf52";
params = SignAuthHelper.sign(params, "test-secret");
assertEquals(expect, params.get("sign"));
System.out.println("Verify Request Body Success");
}
}
