# Common Topics
# 1. How to achieve scaling for services?
Scaling can be done in Deployments without modifying the dice.yml. For details, see Scaling.
Go to DevOps Platform > Projects > App Center > Environments, select a runtime and click Scale out.
![]()
Adjust service resources as needed.
![]()
# 2. Does the service provide an address for internal calls?
Go to DevOps Platform > Projects > App Center > Environments and select a runtime to view the internal address of the service.
Neither service redeployment nor pipeline rebuilding will affect the internal address.

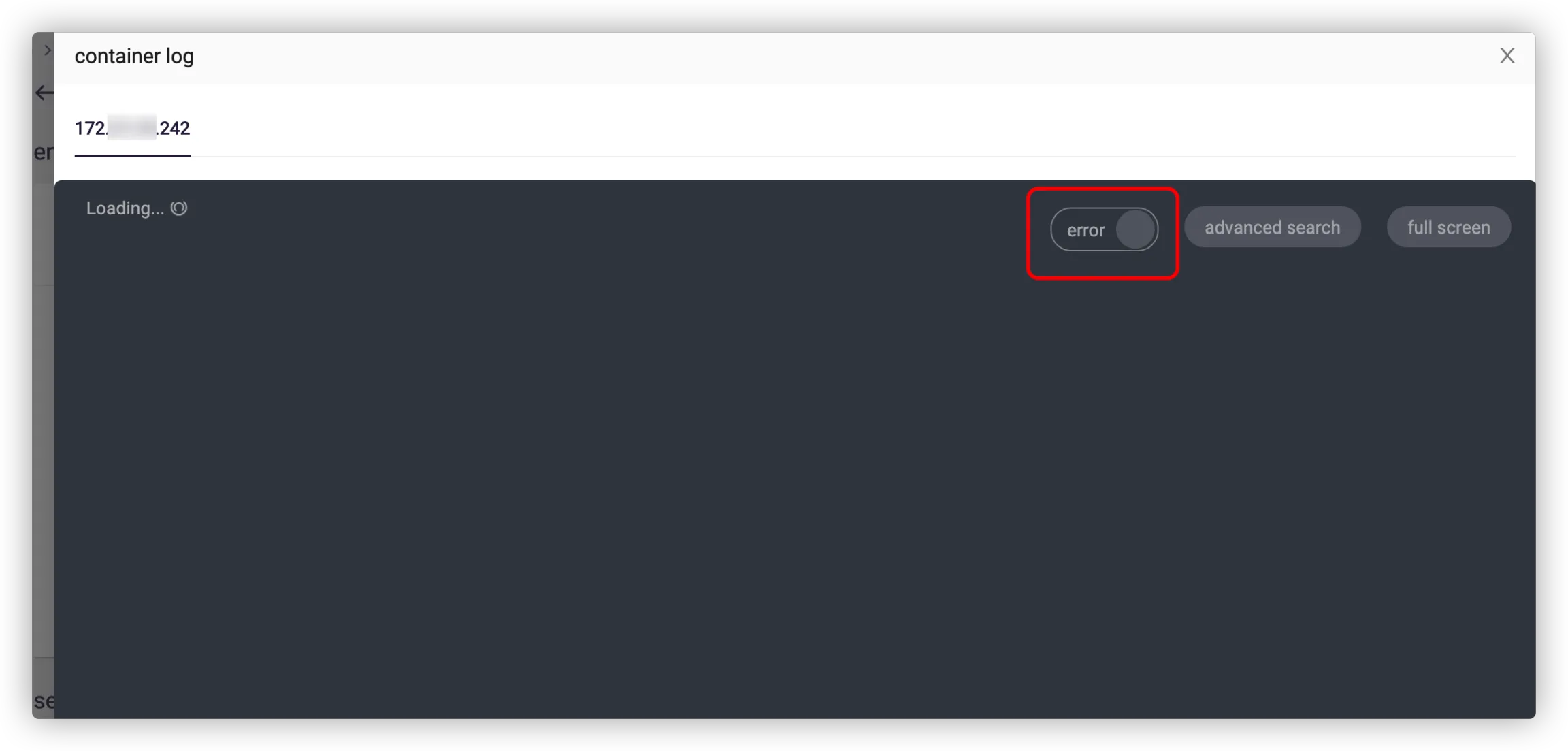
# 3. How to view the error log?
Go to DevOps Platform > Projects > App Center > Environments and select a runtime to view the container log, which shows the standard output (stdout) log. For details, see Service Log.
![]()
Click the switch button to view the standard error (stderr) log.
![]()
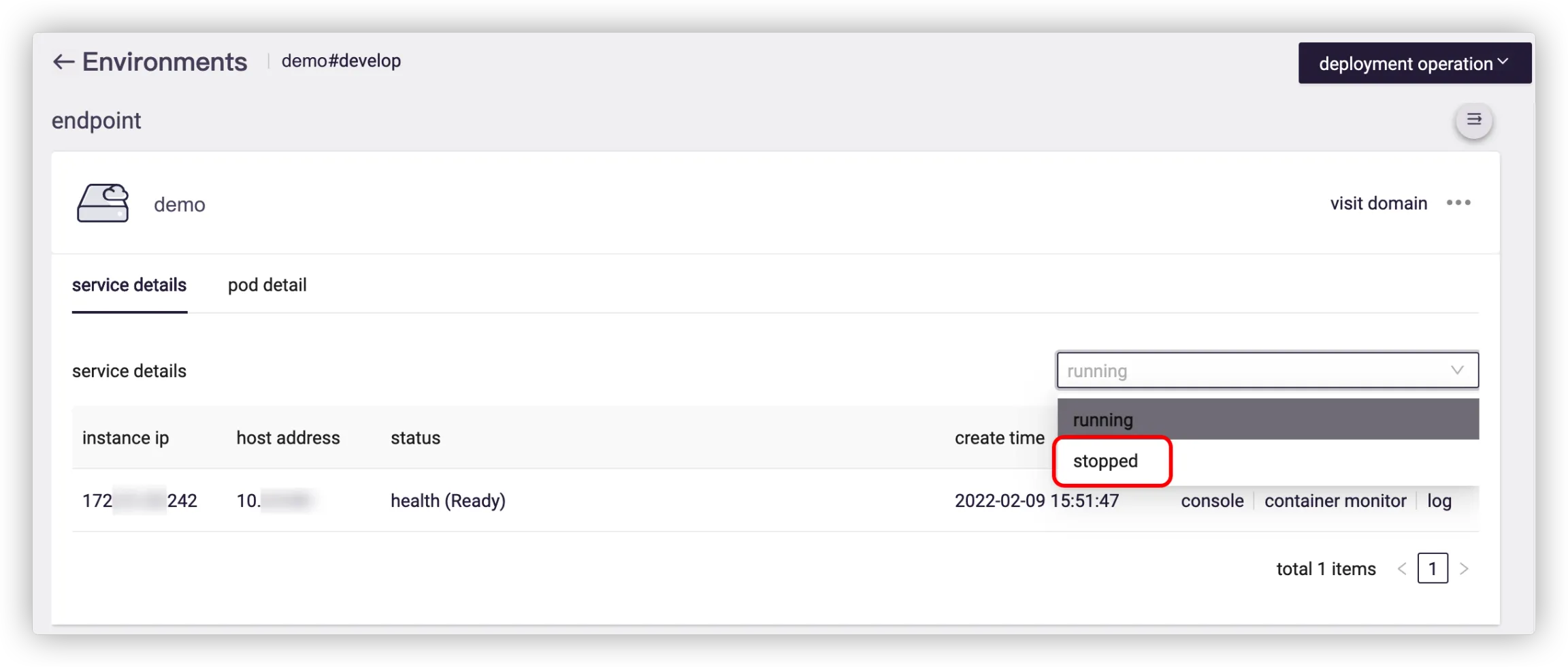
# 4. How to view the stopped container instances?
Go to DevOps Platform > Projects > App Center > Environments, select a runtime and select Stopped to view the corresponding container instance.
![]()
The status bar shows the reason why the container stopped (such as OOM exit, which will be displayed as OOMKilled here). The operate bar allows you to view the resource usage and logs of the container when it is running.
# 5. How to reuse addon?
Reuse an addon based on its name. See the example of dice.yml below, in which redis-abc is the addon name.
addons:
redis-abc:
plan: redis:basic
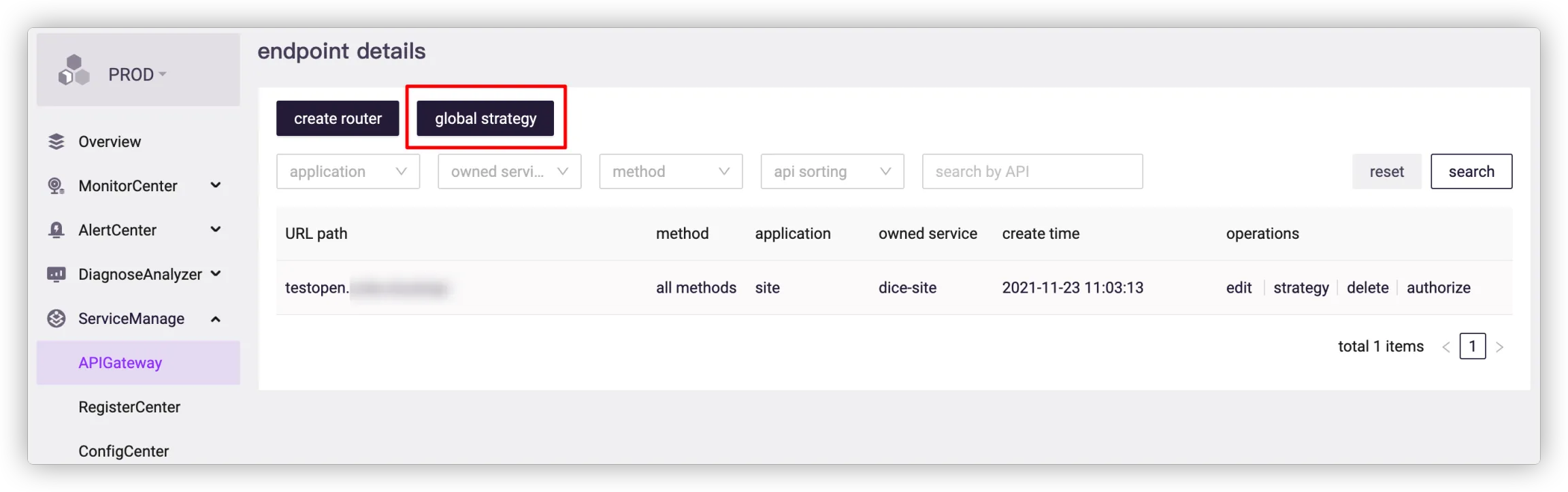
# 6. What should I do if the page redirection fails when using API gateway for forwarding?
The failure is usually due to the use of Host in the request header. It is recommended to use X-Forwarded-Host instead, or to enable the domain name passthrough of the API gateway as follows:
Go to Microservice Platform > Service Management > API Gateway > Endpoints, select an endpoint and click Global Strategy.
![]()
Go to Business Strategy > Traffic Receiving and Forwarding, enable the rule and turn on Domain Name Passthrough.
![]()
# 7. How to achieve force redirection to HTTPS for a specific domain name or API?
Go to Microservice Platform > Service Management > API Gateway > Endpoints, select an endpoint and click Global Strategy or Strategy. (The global strategy is effective for all APIs in the endpoint, and the specific API strategy is only effective for this API.)
![]()
Go to Business Strategy > Traffic Receiving and Forwarding, enable the rule and turn on Force Jump to HTTPS.
![]()
Tips
If port 80 has been configured to force redirect to HTTPS on an external load balancing device such as SLB, the configuration on Erda is invalid.
# 8. How to use storage in containers?
Scenario 1: When multiple containers need to share certain files (such as payment certificates), several instances of an application will share a storage to access the payment certificates. The configuration in dice.yml is as follows:
volumes: - storage: nfs path: /data/certScenario 2: When deploying a service that requires persistent storage (such as Oracle), you can declare a local volume in dice.yml, and the pod will be allocated to the current host again after restarting.
volumes: - storage: local path: /u01/app/oracle
# 9. How to determine the egress IP of a container?
When an application deployed on Erda needs to call an external interface (such as a payment interface), the third-party service usually needs to obtain the egress IP of the public network to locate the problem. Then you can run the following command in the container console:
curl ifconfig.me

# 10. Does the platform support Java 11?
Yes, and you can switch the JDK version of the running container by specifying container_version. Currently JDK 1.8 and 11 are supported.
The configuration in pipeline.yml is as follows:
- java:
params:
build_type: maven # Building type, and Maven is used here
workdir: ${git-checkout} # The working directory for packaging, usually the path of the root pom.xml
options: -am -pl user # Maven packaging parameters, for example, to package the user module, use the command `mvn clean package -am -pl user`, here the command `mvn clean package` is omitted and just fill in the parameters
target: ./user/target/user.jar # The packaged artifact is generally a jar and fill in the relative path compared to workdir. The file is required, otherwise an error will occur.
container_type: spring-boot # Run the container required by target (such as jar). For example, the packaged artifact here is the fat jar of spring-boot, so spring-boot container is used
#container_version: v1.8.0.181 # Optional: v1.8.0.181, v11.0.6, default v1.8.0.181
# 11. What if a prompt occurs indicating that the parameter ClusterName is missing when creating a pipeline?
It means that there are no clusters available in the current environment.
Clusters are necessary for pipeline execution. Please go to DevOps Platform > Projects > Settings > Project Information > Edit to specify a cluster and set quotas for the current environment.
# 12. How to configure a global private Maven repository?
By default, Erda adopts maven.aliyun.com as the Maven repository address, and you can change it as follows:
Edit configmap.
kubectl edit cm dice-addons-info -n erda-systemAdd Maven repository information.
NEXUS_ADDR: # The internal address of the repository, which will be used by the build task in the master cluster NEXUS_PUBLIC_URL: # The external address of the repository, which will be used by the build task in the worker cluster NEXUS_USERNAME: # (Optional) Repository username NEXUS_PASSWORD: # (Optional) Repository passwordWait till the component restarts.
# 13. Front-end project pipeline failure
Generally, switch to the error log to check whether the cause of the error can be located. Common faults are as follows:
- Error log:
Happythread[babel:0] unable to send to worker! ...
Reason: Happypack uses multi-threaded compilation by default, and pipeline jobs running in containers limit build resources and do not support multi-core builds
Solution: Set threads: 1 or ThreadPool({ size: 1 }) in Happypack configuration
- Error log:
npm ERR! code ELIFECYCLE
npm ERR! errno 137
Reason: The process is killed for memory overflow.
Solution: The NPM script corresponding to the build_cmd configured by Action (npm run build by default) is used to set the memory size. If the memory limit is not set, the Node process has a memory limit of 1.4 GB.
The following uses the memory as an example to describe how to use 4G memory for compilation
"build": "webpack --config webpack.config.js"
// 改为
"build": "node --max_old_space_size=4096 ./node_modules/.bin/webpack --config webpack.config.js"
Also set the pipeline action resource size,js-pack action use 1Core 2G by default.
- js-pack:
params:
...
resources:
cpu: 1
mem: 4096
- Debug in container
If you use 'js-pack' action, you can add the following configuration if you can't see the cause from the log
- js-pack:
params:
...
preserve_time: 300 # preserve container for 300 seconds
After the error is occurred, the container will continue to run according to the length of the configuration time.
At the top of the log, it will print content like namespace: pipeline-102679155835278, copy it.
enter the ** cloud management platform > container resources > pods **, selects the cluster of the branch at page top , and then in the name space below, Paste, you should find the pipeline.
Click the record, you can see the container of the pipeline. You can enter the container console, and then debug in container.