# Java
Erda supports building capabilities through a unified task plugin mechanism, and provides Java building plugins out of the box.
# Version
The platform supports Java 1.8 and Java 11, with the former as default.
# Packaging Tool
- Maven
- Gradle
# Dependency Management
If you use the configuration file provided by the platform, you do not need to modify the code. The following files are ready with placeholders filled in.
- Maven: settings.xml
- Gradle: init.gralde
An example of settings.xml is as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<settings xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.0.0.xsd">
<servers>
<server>
<id>terminus</id>
<username>{{NEXUS_USERNAME}}</username>
<password>{{NEXUS_PASSWORD}}</password>
</server>
</servers>
<mirrors>
<mirror>
<id>terminus</id>
<mirrorOf>*</mirrorOf>
<url>{{NEXUS_URL}}/repository/public/</url>
</mirror>
</mirrors>
<profiles>
<profile>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>placeholder</id>
<url>{{NEXUS_URL}}/repository/public/</url>
<releases>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</releases>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
<updatePolicy>always</updatePolicy>
<checksumPolicy>warn</checksumPolicy>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>placeholder</id>
<url>{{NEXUS_URL}}/repository/public/</url>
<releases>
<enabled>true</enabled>
</releases>
<snapshots>
<enabled>true</enabled>
<updatePolicy>always</updatePolicy>
<checksumPolicy>warn</checksumPolicy>
</snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
</profile>
</profiles>
</settings>
An example of init.gradle is as follows:
def NEXUS_SERVER = "{{NEXUS_URL}}/repository/public/"
def NEXUS_USERNAME = "{{NEXUS_USERNAME}}"
def NEXUS_PASSWORD = "{{NEXUS_PASSWORD}}"
allprojects {
buildscript {
repositories {
maven {
credentials {
username NEXUS_USERNAME
password NEXUS_PASSWORD
}
url NEXUS_SERVER
}
}
}
repositories {
maven {
credentials {
username NEXUS_USERNAME
password NEXUS_PASSWORD
}
url NEXUS_SERVER
}
}
}
# Push JAR Package to Private Server
# Upload Maven settings.xml
Go to My Application > Select Application > Setting > Pipeline > Variable Configuration > Select Environment.
Click Add Variable, select the type as File and enable encryption, then upload settings.xml and define the variable name as MAVEN_SETTING_FILE.
Warning
Encryption is required as the file includes sensitive information such as passwords.
An example of settings.xml is as follows:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<settings xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.0.0.xsd">
<servers>
<server>
<id>terminus</id>
<username>deployment</username>
<password>******</password>
</server>
</servers>
</settings>
# Configure Push Address of pom.xml
Add the following configuration to pom.xml of the corresponding project, otherwise it cannot be pushed.
<distributionManagement>
<repository>
<id>terminus</id> <!-- server.id configured in settings.xml -->
<name>Releases</name>
<url>http://private server address/repository/releases</url> <!-- release private server address -->
</repository>
<snapshotRepository>
<id>terminus</id>
<name>Snapshots</name>
<url>http://private server address/repository/releases</url> <!-- snapshot private server address -->
</snapshotRepository>
</distributionManagement>
# Configure Pipeline to Upload JAR Package
MAVEN_SETTING_FILE is the name configured above.
version: "1.1"
stages:
- stage:
- git-checkout:
alias: git-checkout
params:
depth: 1
- stage:
- java-build:
alias: java-build
version: "1.0"
params:
build_cmd:
- "rm -rf /usr/share/maven/conf/setting.xml"
- "mvn clean deploy -e -B -U --settings ((MAVEN_SETTING_FILE)) -Dmaven.test.skip"
jdk_version: 8
workdir: ${git-checkout}
Add configuration of continuous integration (CI) if automated building is required.
on:
push:
branches:
- develop # Continuous integration
Tips
- 401 in Maven indicates incorrect password.
- 405 in Maven possibly indicates incorrect private server address, as some private server addresses cannot be pushed, such as public.
# Push JAR Package to Private Server (Gradle)
# Configure Password of Nexus Private Server
Go to My Application > Select Application > Setting > Pipeline > Variable Configuration > Select Environment.
Click Add Variable, select the type as Value and enable encryption, then configure the following variables:
- NEXUS_USERNAME
- NEXUS_PASSWORD
Warning
Encryption is required as the file includes sensitive information such as passwords.
# Configure Push Address of build.gradle
Add the following configuration to build.gradle of the corresponding project, otherwise it cannot be pushed. For more information, see Configuration of build.gradle (opens new window).
publishing{
...
repositories {
maven {
// change URLs to point to your repos, e.g. http://my.org/repo
def releasesRepoUrl = "http://private server address/repository/releases"
def snapshotsRepoUrl = "http://private server address/repository/snapshots"
url = version.endsWith('SNAPSHOT') ? snapshotsRepoUrl : releasesRepoUrl
credentials {
username = System.getenv("NEXUS_USERNAME")
password = System.getenv("NEXUS_PASSWORD")
}
}
}
}
# Configure Pipeline to Upload JAR Package
version: "1.1"
stages:
- stage:
- git-checkout:
alias: git-checkout
params:
depth: 1
- stage:
- java-build:
alias: java-build
version: "1.0"
params:
build_cmd:
- "./gradlew publish"
jdk_version: 8
workdir: ${git-checkout}
Add configuration of continuous integration (CI) if automated building is required.
on:
push:
branches:
- develop # Continuous integration
Tips
- 401 in Maven indicates incorrect password.
- 405 in Maven possibly indicates incorrect private server address, as some private server addresses cannot be pushed, such as public.
# Access Log
As the platform only collects logs exported to the console, so the application needs to import logs into the console.
Warning
Do not write logs into disk files, which may lead to serious problems such as performance degradation or disk resource exhaustion.
Export logs to the console with Logback configuration:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration scan="true" scanPeriod="30 seconds">
<appender name="CONSOLE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSZZ} [%thread] %-5level %logger{5} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<root level="DEBUG">
<appender-ref ref="CONSOLE"/>
</root>
</configuration>
If the container provided by the platform is used, the platform will automatically close the appenders other than ConsoleAppender such as RollingFileAppender to ensure that the log cannot be written to disk. Please confirm that the ConsoleAppender is configured, otherwise you cannot view the log.
# Building and Packaging
Java building consists of two parts:
- Compile the source code into a packaged product by specified packaging method and context parameters.
- Select images to make JAR package into an operating image according to specified running environment and version.
Tips
It is called packaged product rather than JAR package because of compilation results. For example, traditional Spring MVC program produces WAR package, while gradle distribution produces Tar or ZIP package, run by bin/xxx.
The JAR package made by Spring Boot is called fat jar, as all dependencies except the Java virtual machine are embedded in the JAR package.
Since the fat jar is an all-in-one JAR package, it can run by java -jar app.jar in the Java virtual machine environment.
An example of pipeline.yml is as follows:
version: "1.1"
stages:
- stage:
- git-checkout:
- stage:
- java:
params:
build_type: maven
workdir: ${git-checkout}
options: -am -pl user
target: ./user/target/user.jar
container_type: openjdk
# Packing Acceleration
# Gradle
Comes with Gradle cache node, which is enabled by default.
# Caches
An example is as follows:
- stage:
- java:
caches:
- path: /root/.m2/repository
params:
build_type: maven
workdir: ${git-checkout}
options: -am -pl user
target: ./user/target/user.jar
container_type: openjdk
The directory of /root/.m2/repository is the address of the Maven local repository in Linux, and the building can be accelerated after caching.
# JVM Diagnosis
# Arthas
Arthas can be installed via the curl -sf https://arthas.aliyun.com/arthas-boot.jar -o arthas-boot.jar command.
After the installation is successful, according to the installation directory, execute the java -jar arthas-boot.jar command to start.
For more information on Arthas, see Arthas Documentation (opens new window).
# Greys
If you use the container provided by the platform, Greys is already installed.
For more information on Greys, see Greys Documentation (opens new window).
# Remote Debugging & Hot Update
The platform provides VPNs for local and remote connection to services running on the platform.
To enable remote debugging, go to My Application > Select Application > Setting > Pipeline > Variable Configuration, and add variable configuration for JAVA_OPTS as follows:
JDK 9 and later:
JAVA_OPTS=-agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=*:5005
JDK 5~8:
JAVA_OPTS=-agentlib:jdwp=transport=dt_socket,server=y,suspend=n,address=5005
In addition, if a local IDE is needed, go to DevOps Platform > App Center > Environments to find the container IP, and configure in the IDE as follows:
JDK 9 and later:
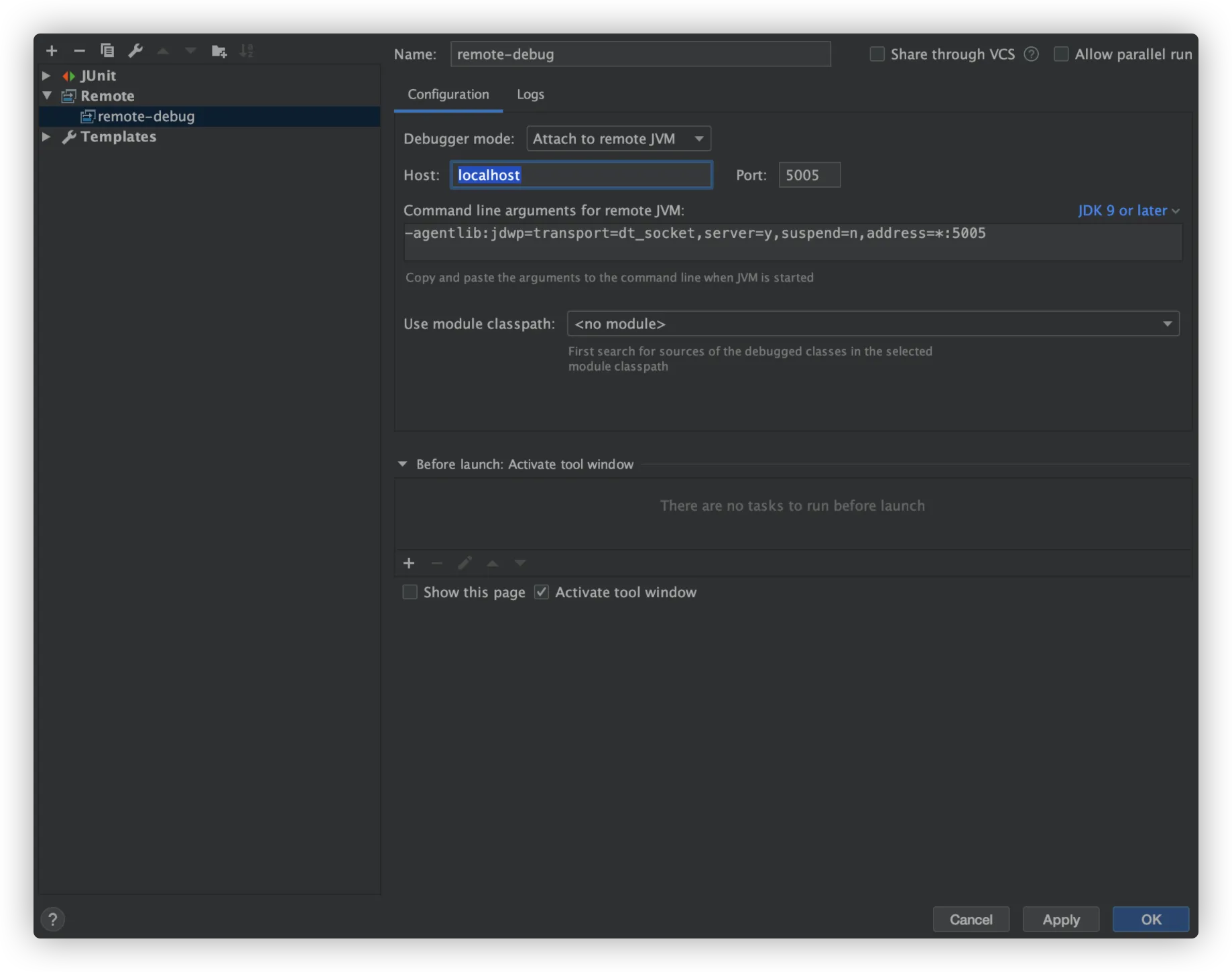
JDK 5~8:

