# Custom Addon
# Application Scenarios
- Non-platform deployed addons (for example, MySQL deployed on a separately purchased machine, etc.)
- Public third-party services (such as SMS channel configuration, etc.)
# Set Entrance
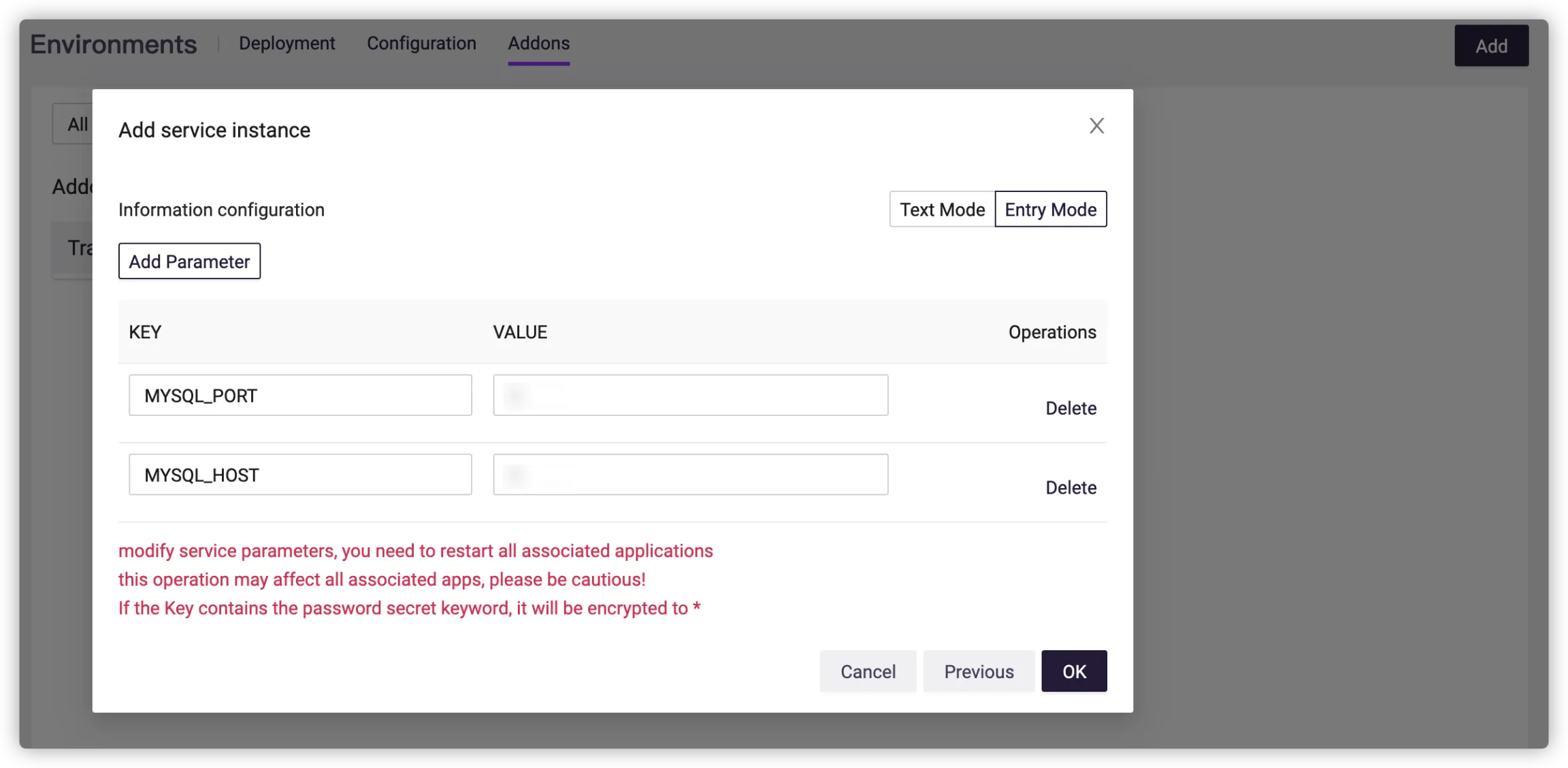
Go to DevOps Platform > Projects > App Center > Environments > Addons, click Add, and select Custom for Third service.

Fill in the configuration.
Tips
After modifying the addon parameters, all associated applications need to be restarted, which may affect these applications. Please operate with caution.
# Use Entrance
Go to Apps > Code, edit the erda.yml and select the previously created addon.
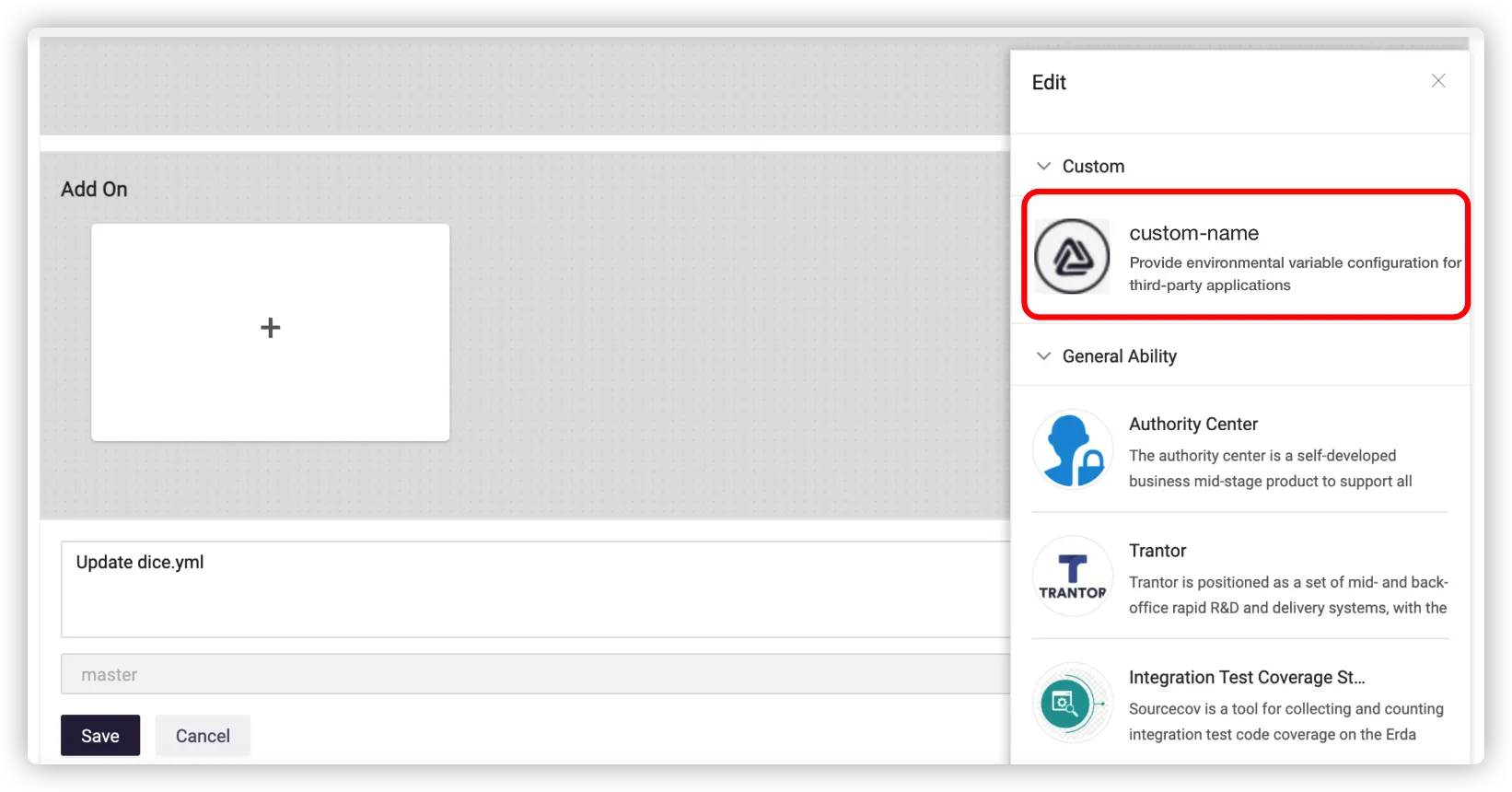
After editing, rebuild and redeploy the pipeline to make the configuration take effect.
# How to Use
The application can obtain configuration through system environment variables. Taking the Spring Boot application as an example, the configuration can be obtained by ${MYSQL_HOST} in application.yml.
server:
port: 8080
spring:
datasource:
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://${MYSQL_HOST:127.0.0.1}:${MYSQL_PORT:3306}/${MYSQL_DATABASE}?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username: ${MYSQL_USERNAME:root}
password: ${MYSQL_PASSWORD:}
# Import and Export
# Export
Go to DevOps Platform > Projects > App Center > Environments > Addons, and click View Config in Custom to view the JSON configuration of all custom addons under the current project.
# Import
Go to DevOps platform > Projects > App Center > Environments > Addons > Add, select Custom for third service and Import Configuration for creation method to paste the exported JSON mentioned above (modify the configuration parameters if necessary), then the custom addon is imported from other projects to the current one.
# Switch Similar Addons Smoothly
In the development phase, developers mostly use the low-cost and out-of-the-box addons on Erda, while in the delivery phase, they want to smoothly switch to a more stable third-party similar addon without modifying the artifact. The similar addon is suitable for such scenarios.
A similar addon is a different presentation of the same function. If you need to use MySQL, you can choose either the third-party addon Alicloud-RDS, or the out-of-the-box erda mysql of Erda. Here the Alicloud-RDS and erda mysql are both for MySQL implementation, and the relationship between the two is similar addon.
When using an out-of-the-box addon of Erda for deployment, the deployed service will preferentially reference the similar addon if there is one under the project with the same name.
Erda supports the following similar addons:
| Type | Third-party | Erda |
|---|---|---|
| MySQL | alicloud-rds | erda mysql |
| Elasticsearch | alicloud-es | terminus-elasticsearch |
| RocketMQ | alicloud-ons | erda rocketmq |
| Redis | alicloud-redis | erda redis |
# Example
You can define the addon in dice.yml or in the artifact. An example of dice.yml is as follows:
addons:
demo-mysql:
plan: "mysql:basic"
demo-es:
plan: "terminus-elasticsearch:basic"
demo-mq:
plan: "rocketmq:basic"
demo-redis:
plan: "redis:basic"
A similar addon with the same name is added to the Addons page, which will be referenced preferentially for service deployment.
Tips
If the service runtime already exists, and you want to switch from an Erda addon to a third-party similar addon (or from a third-party similar addon to an Erda addon), you should first delete the runtime, add (or delete) the third-party similar addon with the same name, and then redeploy it.
